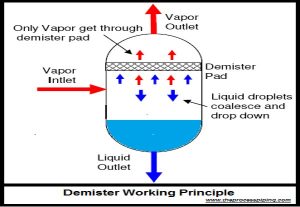
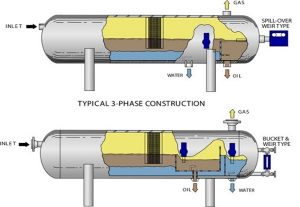
ASME® BPVC Section II, Part A
Is a critical reference document for engineers and designers involved in the construction of pressure vessels and boilers. It provides a comprehensive list of ferrous materials suitable for use in these applications.
Key Material Specifications:
Carbon Steel:
- SA-516: Commonly used for pressure vessel shells and heads.
- SA-285: Used for low-pressure vessels and piping.
- SA-387: High-strength, low-alloy steel for pressure vessels.
Low-Alloy Steel:
- SA-387: Offers improved strength and toughness compared to carbon steel.
- SA-515: Used for high-temperature applications.
Stainless Steel:
- SA-240: Austenitic stainless steel for corrosion resistance.
- SA-249: Ferritic and martensitic stainless steel for high-temperature applications.
Forgings:
- SA-105: Carbon steel forgings.
- SA-336: Low-alloy steel forgings.
- SA-182: Stainless steel forgings.

Pictured above: ASME-SA/516/GR 70 Steel Plate
Material Selection Considerations:
When selecting materials for a pressure vessel or boiler, engineers must consider several factors:
- Strength: The material must be strong enough to withstand the internal pressure and external loads.
- Ductility: The material must be ductile to prevent brittle fracture.
- Toughness: The material must be tough to resist impact loads.
- Corrosion Resistance: The material must be resistant to corrosion from the fluids it will be exposed to.
- Weldability: The material must be weldable using appropriate welding techniques.
- Cost: The cost of the material is also a significant factor.
By carefully selecting materials that meet the specific requirements of the application, engineers can ensure the safety, reliability, and longevity of pressure vessels and boilers.