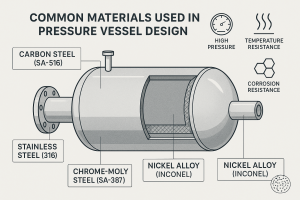
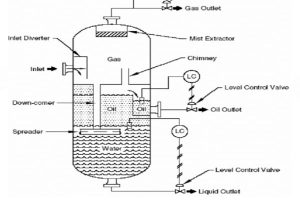
Boiler Code Compliance: A Guide to Meeting Regulatory Standards
When it comes to industrial boilers, cutting corners isn’t just risky—it’s illegal. Code compliance isn’t a formality; it’s a matter of safety, liability, and operational approval. Whether installing a new system or maintaining an existing one, understanding boiler code requirements is essential for any plant engineer, manager, or contractor.
This blog walks through key regulatory standards and best practices to ensure your boiler stays on the right side of the law—and keeps your people and processes safe.
Why Compliance Matters
Boiler explosions and failures are rare today, thanks in large part to rigorous engineering codes and regulatory oversight. Compliance ensures:
- Personnel safety
- Legal operation and insurance coverage
- Inspection readiness
- Avoidance of fines or shutdowns
In some jurisdictions, operating an uninspected or uncertified boiler is considered a criminal offense. It’s that serious.
Pictured above: Boiler Code Compliance
Core Boiler Standards You Should Know
- ASME Boiler and Pressure Vessel Code (BPVC)
The gold standard in North America. ASME Section I covers Power Boilers, and Section IV addresses Heating Boilers.
Key ASME compliance elements include:
- Design calculations and allowable stress
- Material selection and traceability
- Weld procedures and qualifications
- Hydrostatic testing
- Stamping and certification (e.g., “S” stamp, “H” stamp)
- National Board Inspection Code (NBIC)
Covers the installation, inspection, repair, and alteration of boilers and pressure vessels. Often works hand-in-hand with ASME.
- NB registration is often required post-manufacture
- R-Stamp certified contractors are required for certain repairs
- Local Jurisdictional Requirements
Every state or province has its own boiler laws and inspection regimes:
- Annual inspections by certified authorities
- Operator licensing requirements
- Specific emission or control mandates
- Permit and pressure rating thresholds
Always consult the Authority Having Jurisdiction (AHJ) for current rules in your area.
Boiler Compliance Checklist
Here are the essentials every facility should monitor:
✅ Valid ASME code-stamped equipment
✅ Proof of manufacturer data reports (Form U-1, P-2, etc.)
✅ Current operating certificate from local authority
✅ Regular internal and external inspections
✅ Up-to-date safety valve certifications
✅ Operator credentials (if required)
✅ Water treatment logs and boiler maintenance records
✅ Documentation of any repairs, reratings, or alterations
✅ Emergency shutdown procedures clearly posted and tested
Common Compliance Pitfalls
- Letting certificates lapse or failing to post them
- Unauthorized repairs by uncertified personnel
- Operating above MAWP (maximum allowable working pressure)
- Missing documentation for inspections, alterations, or materials
- Improper safety valve sizing or calibration
These issues can result in immediate shutdowns, fines, or denied insurance claims.
Digital Tools for Easier Compliance
In 2025, digital compliance tracking is on the rise. Smart solutions include:
- CMMS platforms to manage inspection schedules and documentation
- Cloud-based inspection logs for real-time audits
- IoT-connected sensors to track operating pressures, trends, and alerts
- QR-coded nameplates linking to vessel history and certifications
These tools reduce admin work while keeping critical compliance data organized and accessible.
Conclusion
Boiler code compliance isn’t just about passing inspections—it’s about designing, operating, and maintaining your system with integrity and accountability. With the right knowledge, documentation, and support, meeting these standards becomes a proactive part of running a safe and efficient operation.
So whether you’re installing your first unit or managing a fleet, remember: compliance is a culture, not just a checklist.