Boiler Maintenance Best Practices: Avoiding Costly Downtime
In industrial operations, boiler downtime isn’t just an inconvenience—it’s a profit killer. Whether it’s lost production, emergency repair costs, or compliance penalties, a boiler failure can have far-reaching impacts. Fortunately, many of these issues are preventable with a strong, proactive maintenance strategy.
In this post, we’ll cover boiler maintenance best practices that help keep systems running safely, efficiently, and reliably—while minimizing surprise shutdowns.
1. Establish a Preventive Maintenance Schedule
Reactive maintenance is a recipe for disaster. Instead, build a preventive maintenance program that includes:
- Daily checks: pressure, temperature, water levels, and combustion efficiency
- Weekly checks: blowdown procedures, burner inspection
- Monthly checks: safety valve operation, chemical levels, controller functionality
- Quarterly/Annual inspections: internal inspection, tube condition, refractory wear
Use OEM recommendations and ASME guidelines as a baseline, and adjust based on usage and environment.
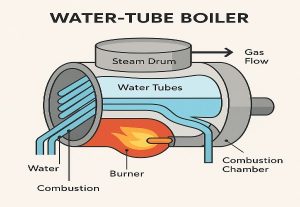
Pictured above: Boiler Maintenance
2. Monitor Water Quality Consistently
Poor water treatment is one of the leading causes of boiler failure. Maintain optimal water chemistry to avoid:
- Scale buildup that reduces heat transfer and stresses components
- Corrosion that weakens tubes and causes leaks
- Foaming and carryover that can damage steam systems
Invest in an automated water treatment system and test regularly. Work closely with a water treatment specialist to tailor a program to your boiler and feedwater source.
3. Blowdown Strategically
Blowdown removes dissolved solids that accumulate in the boiler. Too much, and you waste energy and water. Too little, and you risk scale and corrosion.
- Bottom blowdown removes sludge
- Surface blowdown controls dissolved solids
Automated systems can optimize timing and volume, maintaining system balance while minimizing resource waste.
4. Inspect and Clean Burners
Fuel efficiency drops fast when burners are dirty or out of alignment. Include these in your routine:
- Clean burner tips, pilot assemblies, and igniters
- Check fuel-air ratio and adjust for optimal combustion
- Inspect flame sensors and controls for responsiveness
A tuned burner reduces fuel consumption, emissions, and strain on the boiler.
5. Don’t Ignore Controls and Safety Devices
Your boiler’s brain and nervous system are just as important as the mechanical components. Test and calibrate:
- Pressure and temperature controls
- Flame safeguards
- Safety relief valves
- Low-water cutoffs
Functional safety devices are your last line of defense—never take them for granted.
6. Log Everything
Detailed records help spot trends, anticipate failures, and meet audit or insurance requirements. Keep logs for:
- Operating data (pressures, temps, cycles)
- Maintenance actions
- Water chemistry reports
- Fuel and blowdown usage
Use digital tools or CMMS software to automate alerts, checklists, and compliance tracking.
7. Train Operators Regularly
Even the most automated system needs skilled oversight. Regular operator training improves safety and allows for:
- Faster problem recognition
- Better response during emergencies
- Fewer costly mistakes from unfamiliarity
Refresher courses and cross-training are especially useful in facilities with multiple operators or shifts.
8. Plan for Downtime Before It Happens
Create a contingency plan that includes:
- Spare parts inventory
- Emergency contacts for service contractors
- Isolation procedures and safe shutdown/start-up routines
- Critical path analysis for component failure
Being ready minimizes the time it takes to get back online if the unexpected happens.
Conclusion
Boiler maintenance isn’t glamorous—but it is essential. A well-maintained boiler system is safer, more efficient, and far less likely to let you down when you need it most. By implementing structured preventive practices, investing in training, and staying vigilant with inspections, facilities can save time, money, and headaches down the line.