Electric Boilers: Clean, Compact & Code-Compliant Steam Generation
What is an electric boiler? Learn how it works, when to use one, and what code requirements to follow for inspection and safety.
What Are Electric Boilers?
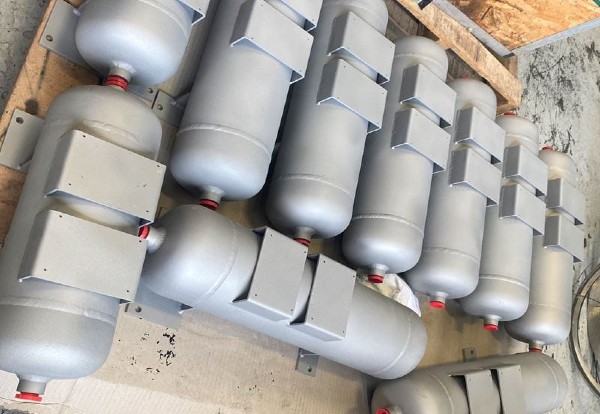
Electric boilers use electricity to generate steam or hot water — eliminating the need for fuel combustion. Unlike traditional boilers, there are no burners, gas valves, or flue stacks. Heat is generated through electrical resistance or electrode-type elements, making them clean, quiet, and often more compact.
Electric boilers are especially popular in buildings, hospitals, clean manufacturing environments, and remote locations where fossil fuels are restricted or not practical.
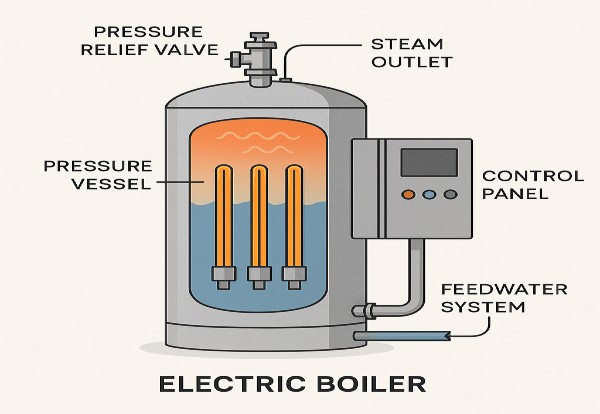
Pictured above: Electric Boiler
How Do They Work
Electric boilers use resistance heating elements or electrodes submerged in water to transfer electrical energy directly into heat. That energy then turns the water into steam or provides hot water for process or comfort heating.
Main Components:
- Pressure vessel or tank
- Heating elements or electrodes
- Control panel & safety systems
- Feedwater system & blowdown controls
Since there’s no combustion, they have fewer moving parts and no exhaust gas management systems.
Why Choose an Electric Boiler?
✅ Zero emissions at the point of use
✅ Ultra-quiet operation — no combustion noise
✅ Precise temperature & pressure control
✅ Lower installation complexity — no flue or venting
✅ Ideal for low-NOx and sustainability-focused projects
With rising pressure on decarbonization and ESG goals, electric boilers are becoming more attractive — especially for facilities with access to clean or low-cost electricity.
Inspection Considerations
Even though there’s no combustion, electric boilers are still pressure-retaining equipment and must be inspected under code guidelines.
- Heating element integrity and mounting
- Pressure relief valve settings and testing
- Water level controls and probes
- Feedwater chemistry to avoid scale and element burnout
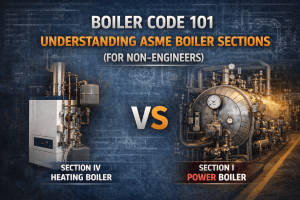
- ASME Section I or IV code stamping
- NBIC R-Stamp records if repairs have occurred
Electric doesn’t mean exempt. It still means inspected.
Code Requirements
Most electric steam generators and hot water heaters are built to ASME Section I (for power boilers) or Section IV (for heating applications). Pressure and temperature thresholds define which section applies.
NBIC requirements still govern repairs, reratings, and alterations — especially when pressure boundaries are involved.
Work closely with electric boiler OEMs and operators to verify compliance and ensure smooth startup, commissioning, and operation.
Are Electric Boilers Right for You?
Electric boilers can be the perfect fit if you need:
- Clean and quiet operation
- Simple installation
- No emissions
- Small space footprint
- Precision control
They’re not for every plant — but for many, they’re a modern solution that aligns with decarbonization, automation, and safety goals.