Floating Head vs. U-Tube Heat Exchangers: A Comparative Analysis
Shell and tube heat exchangers are a common type of heat exchanger used in various industries. Within this category, two primary designs stand out: floating head and U-tube. Each design has its own advantages and disadvantages, making it suitable for specific applications.
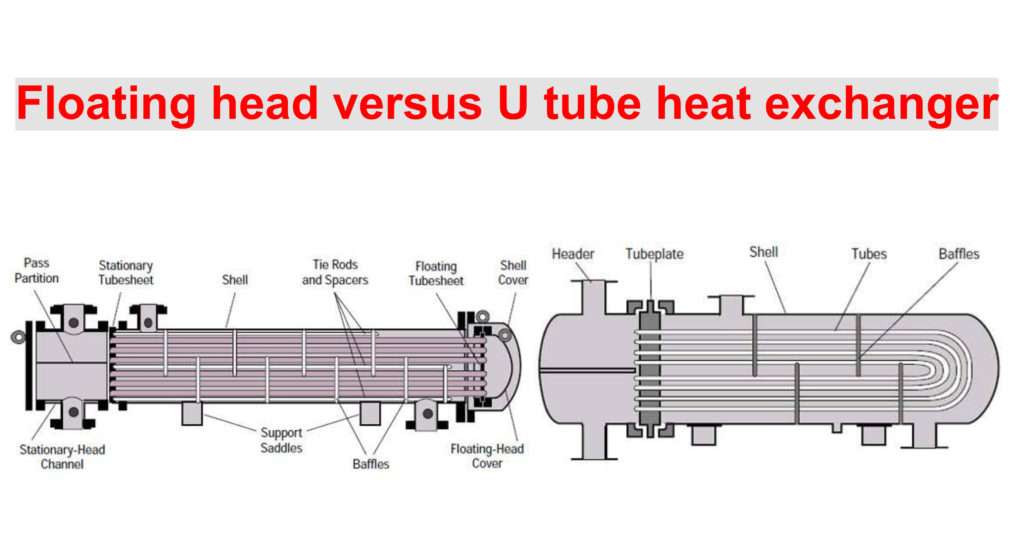
Pictured above: Floating Head vs. U-Tube Heat Exchanger
Design:
- Tube Sheet: One tube sheet is fixed to the shell, while the other is free to move.
- Expansion Joint: A flexible joint allows for thermal expansion and contraction of the tube bundle.
Advantages:
- Accommodates Thermal Expansion: The floating head design can handle significant temperature differences without inducing stress on the tubes or shell.
- High-Pressure Capability: Suitable for high-pressure applications.
- Versatility: Can be used for a wide range of fluids and temperature differences.
Disadvantages:
- Complex Design: More complex to design and manufacture than fixed tube sheet heat exchangers.
- Higher Cost: Typically more expensive due to the additional complexity.
Design:
- Tube Configuration: Tubes are bent into a U-shape, with both ends connected to the same tube sheet.
- Fixed Tube Sheet: Both tube sheets are fixed to the shell.
Advantages:
- Reliable Operation: The U-tube design is less prone to vibration and fatigue failures.
- Ease of Maintenance: Tubes can be easily replaced or cleaned.
- Lower Cost: Generally less expensive than floating head heat exchangers.
Disadvantages:
- Limited Thermal Expansion Capability: The U-tube design can be limited in terms of thermal expansion, especially for high-temperature applications.
- Potential for Vibration: Vibration can occur, especially at high flow rates.
Choosing the Right Design:
The choice between a floating head and U-tube heat exchanger depends on several factors:
- Temperature Difference: For significant temperature differences, a floating head design is preferred to accommodate thermal expansion.
- Pressure Rating: For high-pressure applications, both designs can be used, but the specific design will depend on the pressure rating and temperature range.
- Fluid Compatibility: The materials of construction should be selected based on the fluid compatibility and temperature requirements.
- Maintenance Requirements: Consider the ease of cleaning and tube replacement.
- Cost: The initial cost and ongoing maintenance costs should be evaluated.
Both floating head and U-tube heat exchangers are reliable and efficient solutions for heat transfer. The choice between the two depends on the specific requirements of the application.
By carefully considering these factors, engineers can select the most suitable design for a specific application.