Forced Draft Air Cooler Exchanger: A Versatile Solution for Heat Rejection
Forced draft air cooler exchanger are a type of air-cooled heat exchanger that uses fans to force air across the finned tubes, thereby increasing the rate of heat transfer. They are widely used in various industries, including oil and gas, petrochemical, and power generation, to cool process fluids.
How Forced Draft Air Coolers Work
A forced draft air cooler typically consists of a bundle of finned tubes arranged in a specific configuration. The process fluid flows through the tubes, while air is forced across the fins by fans. The heat from the process fluid is transferred to the air, which is then dissipated into the atmosphere.
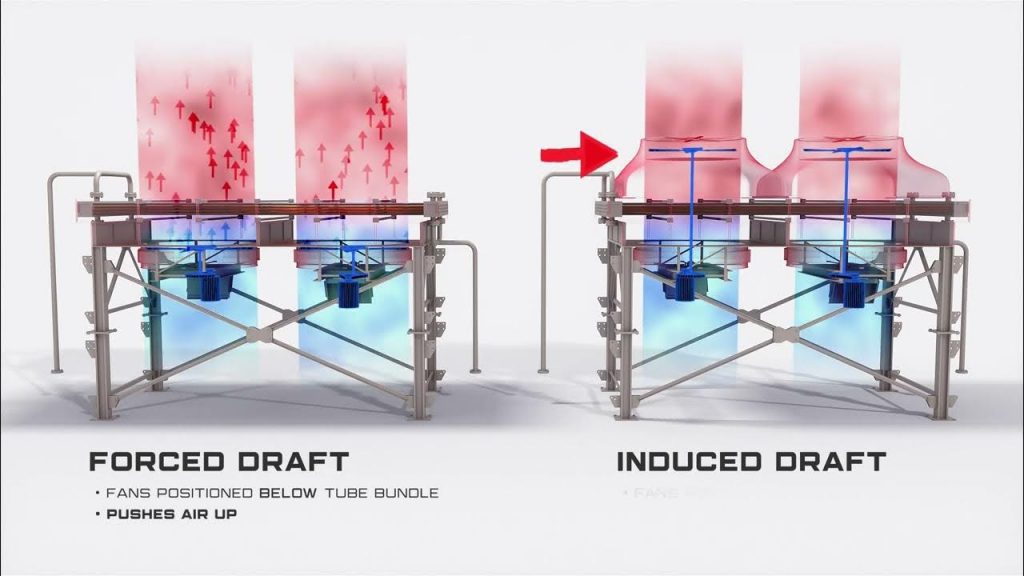
Pictured above: Forced Draft Air Cooler Fan Example
Key Components of a Forced Draft Air Cooler:
- Tube Bundle: The bundle of tubes where the process fluid flows.
- Fins: Extended surfaces attached to the tubes to increase the heat transfer area.
- Fan: A device that forces air across the finned tubes.
- Fan Drive: The motor or turbine that powers the fan.
- Support Structure: A structural framework that supports the tube bundle and fan.
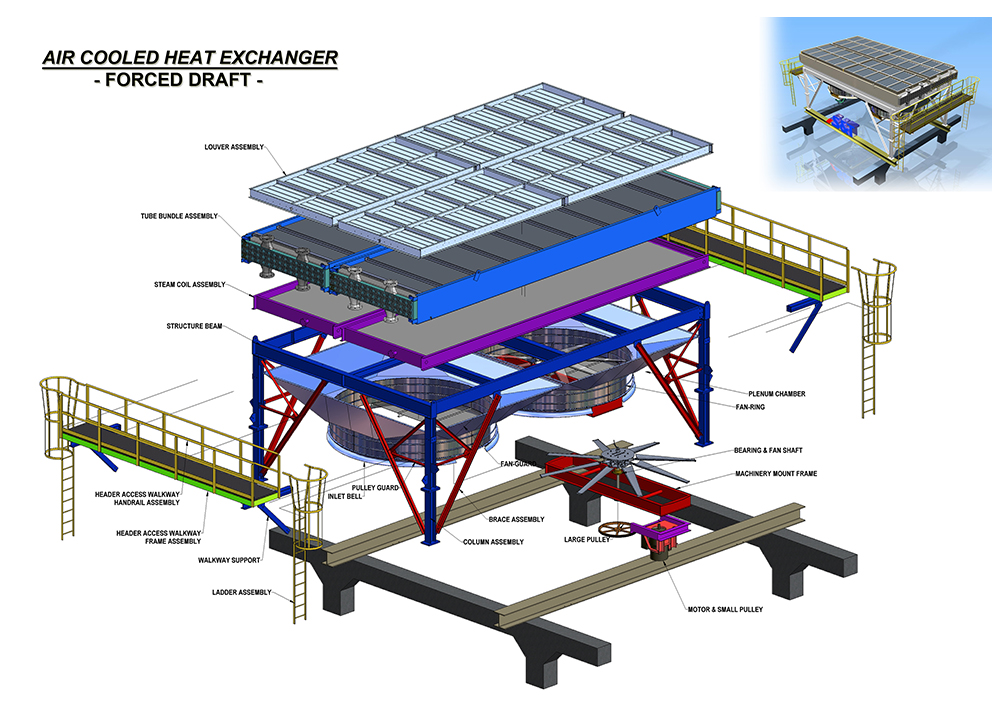
Pictured above: Forced Air Draft Cooler Example
Advantages of Forced Draft Air Coolers:
- Water Conservation: Reduces water consumption by eliminating the need for cooling water.
- Environmental Friendliness: No water discharge or thermal pollution.
- Flexibility: Can be designed for a wide range of capacities and temperature ranges.
- Reliability: Proven technology with a long history of reliable operation.
Disadvantages of Forced Draft Air Coolers:
- Higher Operating Costs: The energy consumption of the fans can increase operating costs.
- Sensitivity to Ambient Conditions: The cooling capacity can be affected by ambient air temperature and humidity.
- Larger Footprint: Requires more space than water-cooled heat exchangers.
Design Considerations for Forced Draft Air Coolers:
- Tube Material: The tube material should be selected based on the fluid compatibility and temperature requirements.
- Fin Material: The fin material should have high thermal conductivity and corrosion resistance.
- Fin Geometry: The fin geometry, including fin height and spacing, affects the heat transfer performance.
- Fan Size and Power: The size and power of the fans determine the airflow rate and cooling capacity.
- Airflow Pattern: The airflow pattern across the tubes can influence the heat transfer efficiency.
- Thermal Hydraulic Design: The design of the heat exchanger must ensure adequate heat transfer and pressure drop.
Forced draft air coolers are a versatile and reliable solution for heat rejection in various industries. Their ability to operate without a water source makes them an attractive option, especially in areas with water scarcity.
By carefully considering these factors, engineers can design forced draft air coolers that meet the specific needs of a particular application.