Induced Draft Air Coolers: A Quiet and Efficient Solution
Induced draft air coolers are a type of air-cooled heat exchanger that uses fans to draw air across the finned tubes. This design offers several advantages over forced draft air coolers, including quieter operation and lower energy consumption.
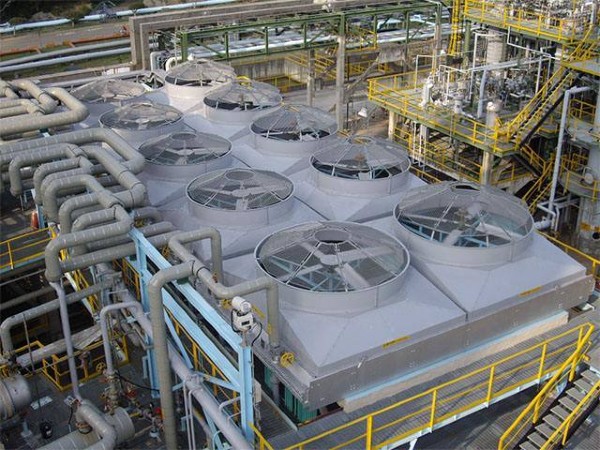

Pictured above: AIR COOLED HEAT EXCHANGER
How Induced Draft Air Coolers Work
In an induced draft air cooler, the fans are located on the outlet side of the tube bundle. This configuration allows the fans to draw air through the heat exchanger, creating a negative pressure within the unit. As a result, air is drawn across the finned tubes, removing heat from the process fluid.
Key Advantages of Induced Draft Air Coolers:
- Quieter Operation: The fans are located on the outlet side, reducing noise levels.
- Lower Energy Consumption: The fans require less power to operate compared to forced draft fans.
- Better Airflow Distribution: The induced draft design can provide more uniform airflow across the tube bundle.
Design Considerations for Induced Draft Air Coolers:
- Fan Size and Power: The size and power of the fans determine the airflow rate and cooling capacity.
- Fan Location: The fans are typically located on top of the heat exchanger.
- Airflow Pattern: The airflow pattern across the tubes can influence the heat transfer efficiency.
- Tube Material and Fin Geometry: As with forced draft air coolers, these factors are crucial for optimal performance.
- Pressure Drop: The pressure drop across the heat exchanger should be minimized to reduce fan power consumption.
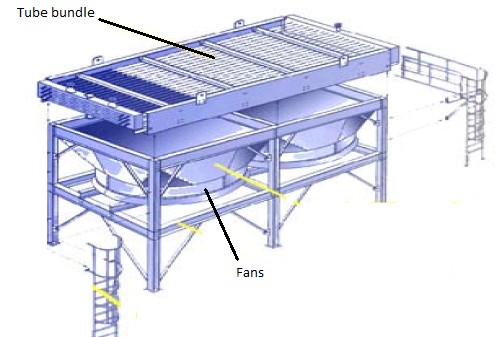
Pictured above: Fan Placement for Induced Draft Air Coolers
Key Differences Between Forced Draft and Induced Draft Air Coolers:
Feature | Forced Draft | Induced Draft |
Fan Location | Inlet side | Outlet side |
Noise Level | Higher | Lower |
Energy Consumption | Higher | Lower |
Airflow Control | More difficult | Easier |
Key Differences Between Forced Draft and Induced Draft Air Coolers:
Feature
- 1. Fan Location
- 2. Noise Level
- 3. Energy Consumption
- 4. Airflow Control
Forced Draft
- 1. Inlet Side
- 2. Higher
- 3. Higher
- 4. More Difficult
Induced Draft
- 1. Outlet Side
- 2. Lower
- 3. Lower
- 4. Easier
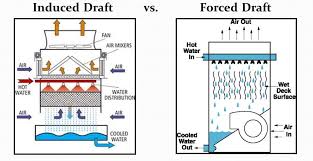
Pictured above: Induced Draft vs Forced Draft
Applications of Induced Draft Air Coolers:
- Oil and Gas: Cooling of process fluids in refineries and petrochemical plants.
- Power Generation: Condensing steam in power plants.
- Chemical Processing: Cooling of process streams.
Induced draft air coolers offer a balance of performance and noise reduction, making them a popular choice for many industrial applications.
By carefully considering these factors, engineers can design induced draft air coolers that are both efficient and quiet.