Natural Draft Air Cooler Exchanger: A Sustainable Solution for Heat Rejection
Natural Draft Air Cooler Exchanger are a type of air-cooled heat exchanger that relies on natural convection to draw air across the finned tubes. This technology offers a sustainable and energy-efficient solution for heat rejection, making it a popular choice in various industries.
The natural draft cooling towers are commonly used in industrial facilities where the total heat rate is at the level of approximately 450 MW. Their draft given by height and dimensions of the stack reduces operating costs and energy consumption costs. Other advantages of this kind of cooling tower include long service life, low noise emissions, and low maintenance demands.
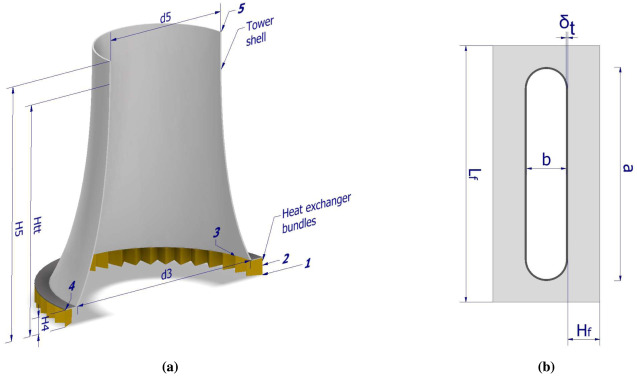
Pictured above: Natural Draft Air Coolers
How Natural Draft Air Coolers Work
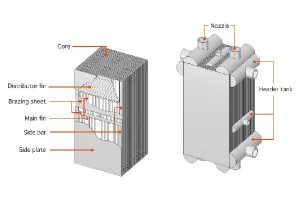
A natural draft air cooler typically consists of a tall, tower-like structure with a large number of finned tubes. The hot process fluid flows through the tubes, and the heat is transferred to the surrounding air. The heated air rises due to natural convection, drawing in cooler air from the surroundings.
The natural draft cooling towers, sometimes called “Iterson”, are used in the same way as the forced draft cooling towers for removing low-potential heat generated in the production process. The cooling principle is the same (atmospheric cooling with wet technology), but the fan unit is missing here since heat is removed from the cooling tower using a natural draft. Natural draft cooling towers are always designed based on the specific customer needs, and they comply with required parameters and specific conditions at the installation site.
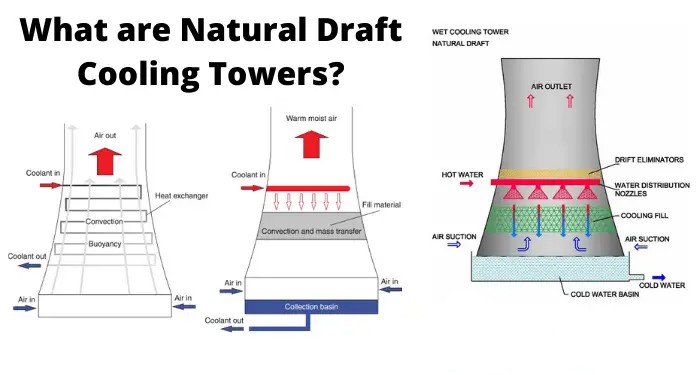
Pictured above: Description of a “What are Natural Draft Cooling Tower”
Key Components of a Natural Draft Air Cooler:
- Tube Bundle: The bundle of tubes where the process fluid flows.
- Fins: Extended surfaces attached to the tubes to increase the heat transfer area.
- Chimney: A tall chimney that creates a draft to draw air through the heat exchanger.
Other Components
- support body of hyperbolic shape (reinforced concrete, steel)
- sheathing
- cooling fill
- drift eliminators
- water distribution system including sprying nozzles
- water basin
Advantages of Natural Draft Air Coolers:
- No Fan Power: Relies on natural convection, eliminating the need for fans and reducing energy consumption.
- Low Maintenance: Simple design with minimal moving parts.
- Environmental Friendliness: No water consumption or thermal pollution.
- Reliable Operation: Proven technology with a long history of reliable performance.
Disadvantages of Natural Draft Air Coolers:
- Large Footprint: Requires a significant amount of land.
- Limited Cooling Capacity: The cooling capacity is limited by the natural draft.
- Sensitivity to Ambient Conditions: The performance can be affected by ambient air temperature and wind conditions.
Design Considerations for Natural Draft Air Coolers:
- Chimney Height: The height of the chimney affects the draft and cooling capacity.
- Tube Bundle Configuration: The arrangement of the tubes and fins influences the heat transfer performance.
- Airflow Pattern: The airflow pattern through the heat exchanger should be optimized for efficient heat transfer.
- Material Selection: The materials of construction should be selected to withstand the operating conditions and minimize corrosion.
Natural draft air coolers offer a sustainable and energy-efficient solution for heat rejection. While they may require a larger footprint compared to other types of air-cooled heat exchangers, their low operating costs and minimal environmental impact make them an attractive option in many applications.
By carefully considering these factors, engineers can design natural draft air coolers that meet the specific needs of a particular application.