Modular Boilers: Scalable Steam Systems with Built-In Flexibility
Explore how modular boilers work, their benefits in industrial settings, and what to inspect for safe, code-compliant operation.
What Are Modular Boilers?
Modular boilers are compact, factory-assembled boiler units designed to work together in a series — offering scalable steam or hot water generation based on demand. Rather than relying on a single large boiler, modular systems operate with multiple small units that can be staged on or off as needed.
Each module is typically rated under 300,000 to 1,000,000 BTU/hr and is often built to ASME Section IV (for heating boilers), though some high-pressure systems fall under Section I.
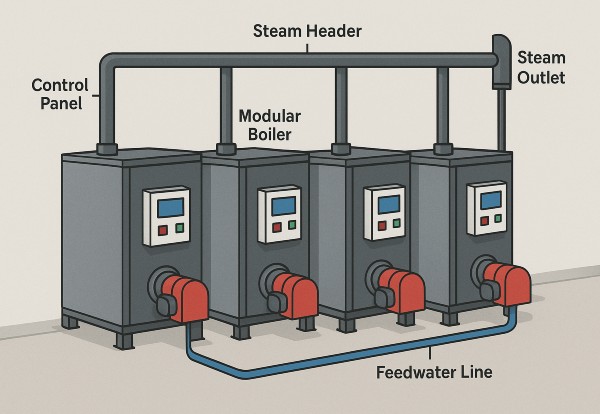
Pictured above: Modular Boiler
How Do They Work?
A modular boiler system consists of 2 or more smaller boilers connected in parallel. A control system monitors demand and brings modules online in stages — allowing the plant to match load precisely while maximizing efficiency.
Key Components:
- Individual boiler modules (gas or electric)
- Central control panel
- Header piping for steam or hot water
- Feedwater and blowdown systems
- Vent or stack systems for combustion units
Systems can be floor-mounted or skid-mounted for easy installation.
Benefits of Modular Boilers
✅ Scalability — add modules as your load grows
✅ Redundancy — if one unit goes down, others stay running
✅ Energy efficiency — only run what you need
✅ Compact footprint — fits in tight mechanical rooms
✅ Quick install & maintenance — pre-engineered and standardized
✅ Fast startup — reach setpoints quicker than large boilers
They’re ideal for schools, hospitals, multi-tenant buildings, commercial laundries, and light industrial operations.
Inspection Focus for Modular Boilers
While smaller in size, modular boilers still fall under inspection requirements — especially when the system exceeds 100 kW (≈ 340 MBH) or when individual modules are ASME stamped pressure vessels.
Authorized Inspector reviews typically include:
- Nameplate & ASME stamping on each module
- Piping header integrity and pressure rating
- Pressure relief valves on each pressure vessel
- Feedwater/condensate systems (especially shared ones)
- Control logic and sequencing safeties
- NBIC documentation if repairs or alterations were made
Modules operating under shared pressure headers must still meet jurisdictional and ASME code requirements.
Code Requirements for Modular Boilers
Depending on pressure and service:
- ASME Section I applies for high-pressure steam systems
- ASME Section IV applies for low-pressure heating boilers
- NBIC governs repairs, rerates, and installation records
- Some jurisdictions require Authorized Inspector signoff on modular system assemblies — not just the modules themselves
Ideal Applications for Modular Boiler Systems
- Commercial buildings with fluctuating loads
- Hospitals and medical campuses
- Schools and universities
- Breweries and food processing
- Facilities prioritizing resilience and expansion-ready infrastructure