A Simple and Reliable Solution
Double-Pipe Heat Exchangers: A Simple and Reliable Solution
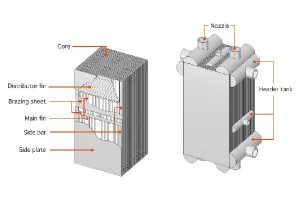
Double-pipe heat exchangers are a simple yet effective type of heat exchanger that consists of two concentric pipes. One fluid flows through the inner pipe, while the other fluid flows through the annular space between the two pipes. This design provides a compact and efficient solution for many heat transfer applications.
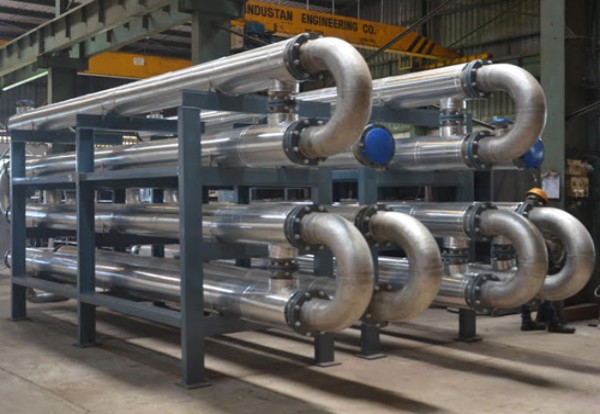

Pictured above: Double-Pipe Heat Exchangers
How Double-Pipe Heat Exchangers Work
In a double-pipe heat exchanger, heat is transferred between the two fluids through the pipe wall. The fluids can flow in either a parallel-flow or counter-flow arrangement. Counter-flow arrangement generally provides higher heat transfer efficiency.
Key Components of a Double-Pipe Heat Exchanger:
- Inner Pipe: The smaller pipe through which one fluid flows.
- Outer Pipe: The larger pipe that encloses the inner pipe.
- Baffles (Optional): Baffles can be added to the annular space to improve heat transfer efficiency.
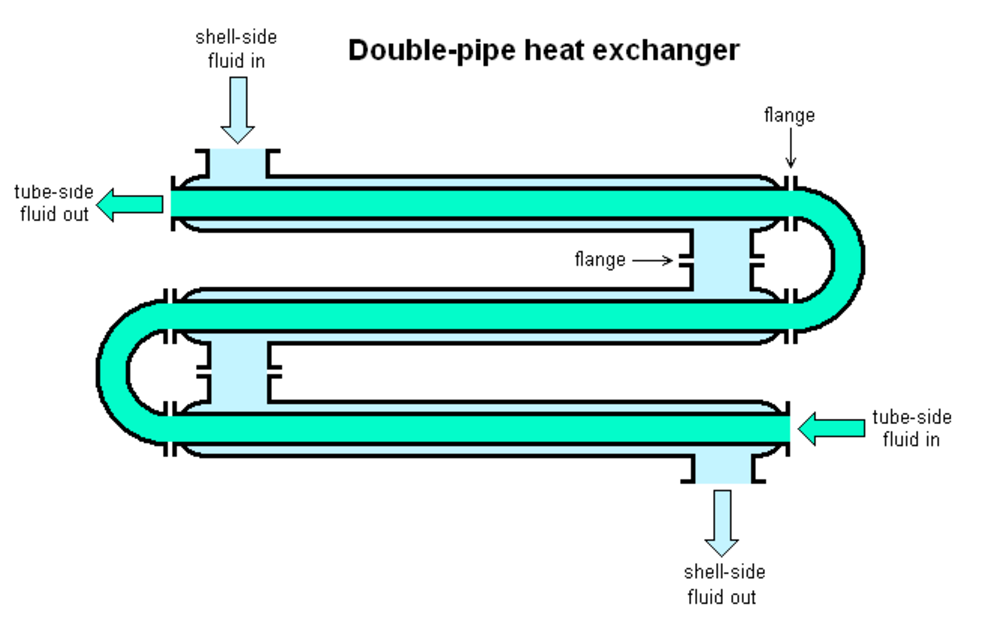
Pictured above: How Double-Pipe Heat Exchangers Work
Advantages vs Disadvantages of a Double-Pipe Heat Exchangers Work
Advantages
- Simple Design: Easy to design, fabricate, and maintain.
- Reliable Operation: Proven technology with a long history of reliable performance.
- Compact Design: Requires less space compared to other types of heat exchangers.
- Versatility: Can handle a wide range of fluids and temperature differences.
Disadvantages
- Limited Heat Transfer Area: The heat transfer area is limited by the surface area of the pipes.
- Potential for Fouling: The inner pipe can become fouled with deposits, reducing heat transfer efficiency.
- Limited Pressure Rating: May not be suitable for high-pressure applications.
Design Considerations
- Pipe Material: The pipe material should be selected based on the fluid compatibility and temperature requirements.
- Pipe Diameter: The diameter of the pipes affects the heat transfer area and pressure drop.
- Baffle Spacing and Type: The spacing and type of baffles can influence the heat transfer efficiency and pressure drop.
- Flow Arrangement: The choice of parallel flow or counterflow arrangement affects the overall heat transfer performance.
- Fluid Velocity: The fluid velocity in the pipes affects the heat transfer coefficient.
Double-pipe heat exchangers are a simple and reliable solution for a wide range of heat transfer applications. While they may have limitations in terms of heat transfer capacity, they are often a cost-effective choice for smaller-scale applications.
By carefully considering these factors, engineers can design double-pipe heat exchangers that meet the specific needs of a particular application.