Filter Separators: A Versatile Solution for Solid-Liquid Separation
Filter separators are widely used in various industries to remove solid particles from liquid streams. They are essential for maintaining product quality, protecting downstream equipment, and ensuring efficient processes.
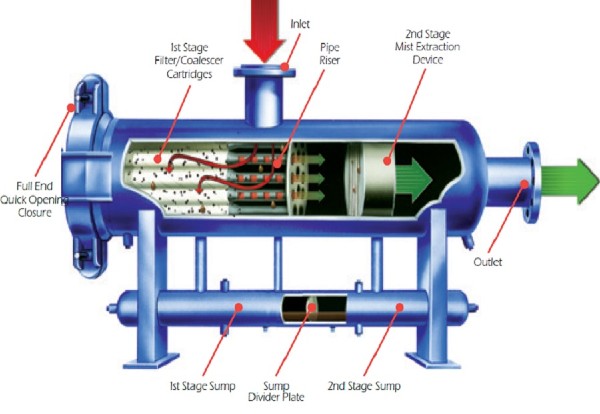
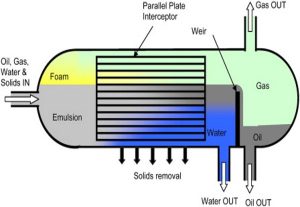
Pictured above: Filter Separator
Types of Filter Separators
Gravity Filters:
- Simple Gravity Filters: These filters use gravity to separate solid particles from a liquid. The liquid flows through a filter medium, such as sand or cloth, which traps the solid particles.
- Clarifiers: These are large sedimentation tanks that use gravity to settle solid particles.
Pressure Filters:
- Plate and Frame Filters: These filters consist of a series of plates and frames, with filter cloth between them. The liquid is forced through the filter cloth, trapping the solid particles.
- Cartridge Filters: These filters use disposable cartridges containing filter media, such as depth filters or membrane filters.
- Bag Filters: These filters use bags made of filter media to remove solid particles.
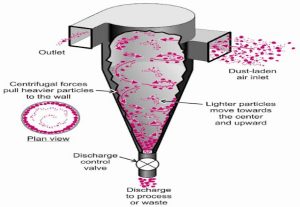
Centrifugal Filters:
- Disc Stack Centrifuges: These filters use centrifugal force to separate solid particles from a liquid. The liquid is forced through a stack of discs, which trap the solid particles.
Design Considerations for Filter Separators
The design of a filter separator involves several key factors:
- Filter Media: The choice of filter media depends on the particle size, shape, and concentration, as well as the liquid properties.
- Filter Area: The filter area determines the capacity of the separator.
- Flow Rate: The flow rate of the liquid affects the pressure drop across the filter and the required filter area.
- Pressure Drop: The pressure drop across the filter should be minimized to reduce energy consumption.
- Filtration Efficiency: The filter should be able to remove particles of a specific size and concentration.
- Cleaning and Maintenance: The filter should be easy to clean and maintain.
Key Design Data:
- Filter Media: Porosity, thickness, and filtration efficiency.
- Filter Area: Total surface area of the filter medium.
- Flow Rate: Volumetric flow rate of the liquid.
- Pressure Drop: Pressure difference across the filter.
- Filtration Velocity: The velocity of the liquid through the filter medium.
Applications of Filter Separators
Filter separators are used in a wide range of industries, including:
- Water Treatment: Removing suspended solids and turbidity from water.
- Oil and Gas: Separating oil, water, and solid particles from produced fluids.
- Chemical Processing: Filtering process streams to remove impurities.
- Food and Beverage: Filtering beverages and other food products.
- Pharmaceutical Industry: Filtering pharmaceutical products.
By carefully considering the design factors and selecting the appropriate filter separator, engineers can ensure efficient and effective solid-liquid separation.