Mix Exchangers: Blending Efficiency and Energy Conservation
Mix Exchangers are a type of heat exchanger that combines two or more fluid streams to achieve a desired temperature or composition. They are widely used in various industries, including chemical processing, petroleum refining, and power generation.
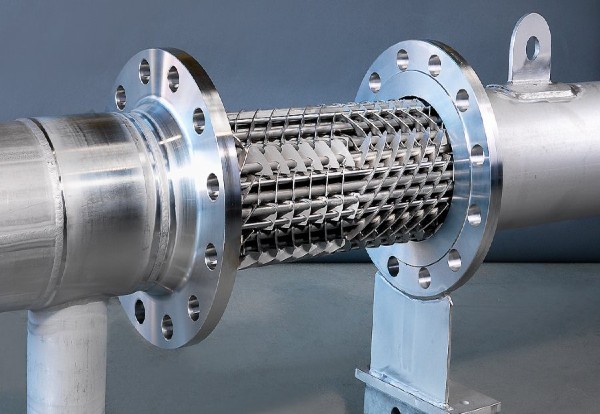
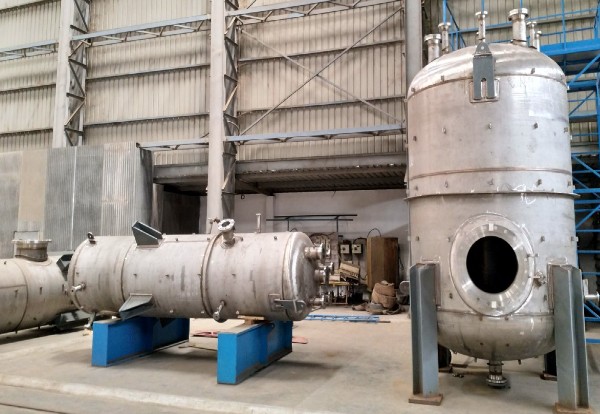
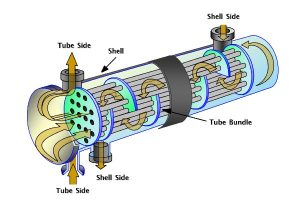
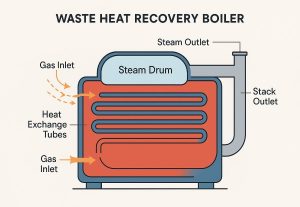
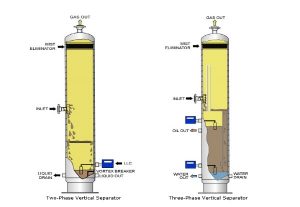
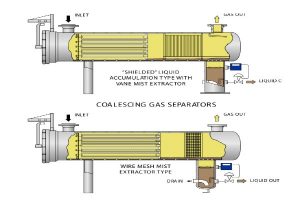
Pictured above: Mix Exchanger
How Mix Exchangers Work
- Static Mixers: These devices use a series of static elements to induce turbulence and promote mixing.
- Dynamic Mixers: These devices use rotating elements to create turbulence and enhance mixing.
Key Design Considerations for Mix Exchangers:
- Mixing Efficiency: The design should ensure thorough and rapid mixing of the fluids.
- Pressure Drop: The pressure drop across the mixer should be minimized to reduce pumping power requirements.
- Material Compatibility: The materials of construction should be compatible with the fluids being mixed.
- Corrosion Resistance: The materials should be resistant to corrosion from the fluids.
- Fouling Resistance: The design should minimize fouling and provide easy cleaning.
- Scale-up: The design should be scalable to accommodate different flow rates and fluid properties.
Design Data for Mix Exchangers
The design of a mix exchanger involves several key parameters:
- Flow Rate: The flow rates of the individual streams.
- Fluid Properties: The density, viscosity, and temperature of the fluids.
- Mixing Intensity: The degree of mixing required to achieve the desired outcome.
- Pressure Drop: The allowable pressure drop across the mixer.
- Material Compatibility: The compatibility of the fluids with the materials of construction.
Applications of Mix Exchangers:
- Temperature Control: Mixing hot and cold fluids to achieve a desired temperature.
- Blending: Mixing different components to create a specific blend.
- Dilution: Diluting concentrated solutions.
- Reaction Quenching: Rapidly cooling reaction products.
Mix exchangers play a critical role in many industrial processes. By understanding the key design considerations and selecting the appropriate type of mixer, engineers can optimize the performance of these devices.