Plate and Frame Heat Exchangers
A Compact and Efficient Solution
Plate and frame heat exchangers are a type of heat exchanger that uses a series of corrugated plates to transfer heat between two fluids. The plates are stacked together, forming narrow channels through which the fluids flow. This design allows for a large heat transfer surface area in a compact footprint.
How They Work
In a plate and frame heat exchanger, the two fluids flow through alternate channels formed by the corrugated plates. The corrugated pattern increases the turbulence of the fluid flow, enhancing heat transfer. The plates are clamped together within a frame, creating a sealed assembly.
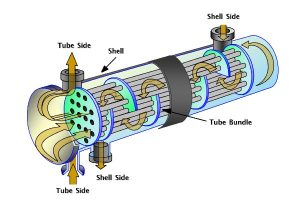
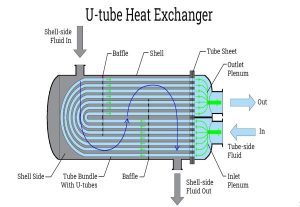
Pictured above: Plate and Frame Heat Exchanger workings
Advantages vs Disadvantage of a Plate and Frame Heat Exchangers:
Advantages:
- High Heat Transfer Efficiency: The large surface area and turbulent flow enhance heat transfer.
- Compact Design: Plate and frame heat exchangers are more compact than shell and tube heat exchangers.
- Easy Cleaning: The plates can be easily removed for cleaning or replacement.
- Versatility: Can handle a wide range of fluids and temperature differences.
- Low Maintenance: Requires minimal maintenance.
Disadvantages:
- Susceptibility to Fouling: The plates can become fouled with deposits, reducing heat transfer efficiency.
- Limited Pressure Rating: Typically limited to lower pressure applications.
- Potential for Leakage: The gaskets between the plates can leak if not properly maintained.
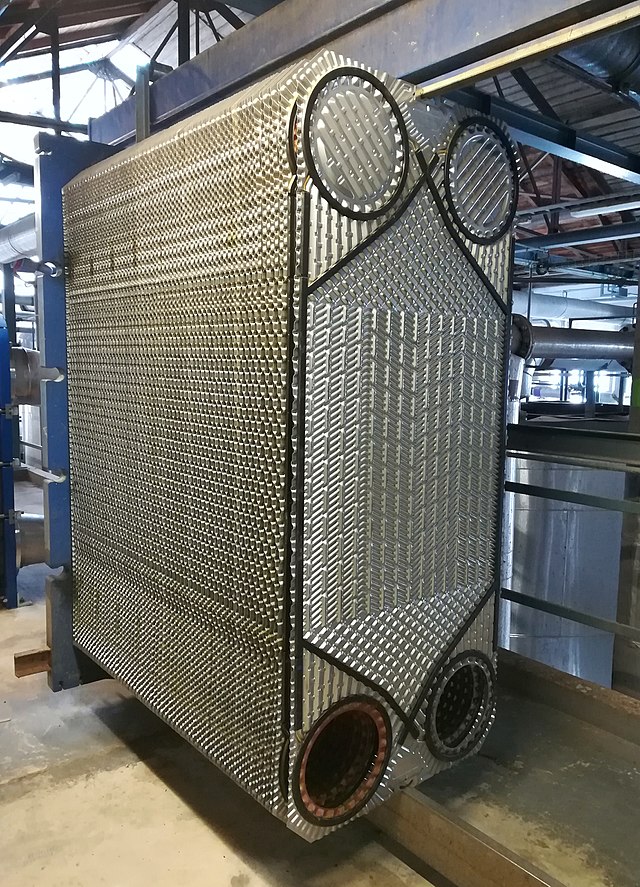

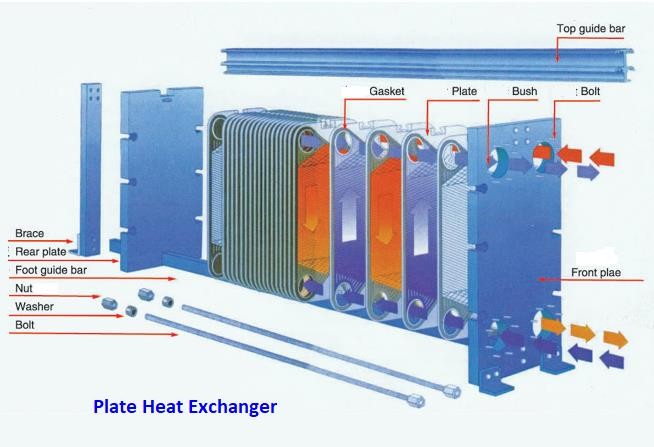
Pictured above: Plate heat exchanger dismantled
Key Considerations for Design and Selection:
- Plate Material: The plate material should be selected based on the fluid compatibility and temperature requirements.
- Plate Pattern: The pattern of corrugations on the plates can influence the heat transfer performance.
- Gasket Material: The gasket material should be selected to provide a good seal and resist the operating conditions.
- Plate Thickness: The plate thickness must be sufficient to withstand the operating pressure.
- Frame Design: The frame must be strong enough to withstand the pressure and thermal stresses.
Plate and frame heat exchangers are a versatile and efficient solution for many heat transfer applications. Their compact design, high heat transfer efficiency, and ease of maintenance make them a popular choice in various industries.
By carefully considering these factors, engineers can select and design plate and frame heat exchangers that meet the specific needs of a particular application.