A Solution for Challenging Fluids
Scraped Surface Heat Exchangers
Scraped surface heat exchangers are specialized heat exchangers designed to handle highly viscous fluids, slurries, and materials with a tendency to foul. They are particularly effective in applications where conventional heat exchangers struggle to maintain efficient heat transfer.
How They Work
A scraped surface heat exchanger consists of a cylindrical shell with a rotating shaft inside. The shaft is fitted with blades or scrapers that continuously scrape the inner surface of the shell. This scraping action prevents the formation of product buildup on the heat transfer surface, ensuring efficient heat transfer.
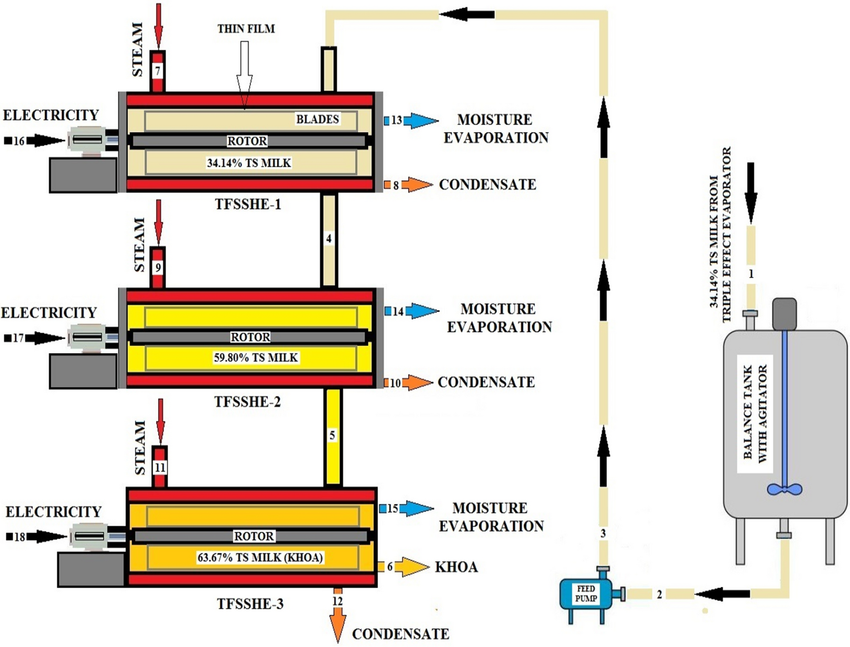
Pictured above: Schematics of Scraped Surface Heat Exchanger-for-Milk-Food
Key Components
- Shell: The outer cylindrical casing that encloses the rotating shaft and blades.
- Shaft: A rotating shaft that carries the blades or scrapers.
- Blades or Scrapers: These elements scrape the inner surface of the shell to prevent fouling.
- Heating or Cooling Medium: The fluid used to heat or cool the process fluid.
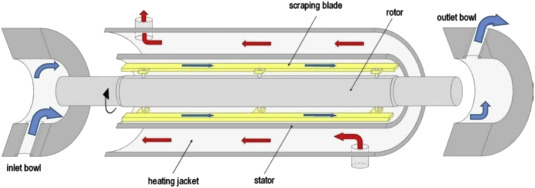
Pictured above: Scraped Surface Heat Exchangers
Advantages of a Scraped Surface Heat Exchangers:
- Efficient Heat Transfer: The continuous scraping action prevents fouling and maintains high heat transfer efficiency.
- Handling Viscous Fluids: Can handle highly viscous fluids that are difficult to pump.
- Crystallization Prevention: Prevents crystallization and fouling, especially in applications involving temperature changes.
- Versatility: Can be used for heating, cooling, and evaporation processes.
Design Considerations
- Shaft Speed: The speed of the shaft affects the scraping efficiency and heat transfer rate.
- Blade Design: The design of the blades or scrapers influences the scraping effectiveness and pressure drop.
- Shell Material: The shell material should be selected based on the fluid compatibility and temperature requirements.
- Shaft Seal: The shaft seal must be designed to prevent leakage and withstand the operating conditions.
- Heating or Cooling Medium: The choice of heating or cooling medium will depend on the specific application.
Applications of Scraped Surface Heat Exchangers:
- Food Processing: Pasteurization, sterilization, and concentration of food products.
- Chemical Processing: Reactions involving viscous fluids or slurries.
- Pharmaceutical Industry: Production of pharmaceuticals and biopharmaceuticals.
- Paper Industry: Cooking and drying of paper pulp.
- Polymer Processing: Extrusion and molding of polymers.
Scraped surface heat exchangers are a valuable tool for industries that deal with difficult-to-handle fluids. Their ability to maintain high heat transfer efficiency and prevent fouling makes them a reliable and efficient solution.
By understanding the design principles and advantages of scraped surface heat exchangers, engineers can select and design these heat exchangers to meet the specific needs of challenging applications.