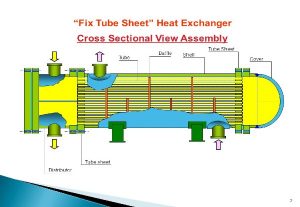
A Solution for Challenging Applications
Spiral Heat Exchangers: A Compact and Efficient Solution
Spiral heat exchangers are a specialized type of heat exchanger that offer numerous advantages over traditional shell-and-tube and plate-and-frame designs. They are particularly well-suited for handling viscous fluids, slurries, and fouling services.
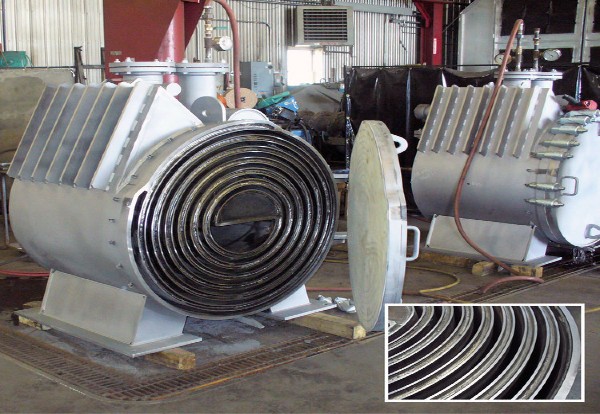

Pictured above: Sludge Spiral Heat Exchanger
How Spiral Heat Exchangers Work
A spiral heat exchanger consists of two spiral-wound channels, one for each fluid. The two channels are separated by a partition, and the fluids flow in opposite directions through the channels. This counter-current flow arrangement maximizes heat transfer efficiency.
Key Advantages
- High Heat Transfer Efficiency: The spiral design and counter-current flow promote efficient heat transfer.
- Self-Cleaning: The spiral channels can self-clean, reducing the need for frequent maintenance.
- High Pressure Capability: Spiral heat exchangers can handle high-pressure applications.
- Compact Design: They require less floor space compared to other types of heat exchangers.
- Versatility: Can handle a wide range of fluids, including viscous fluids and slurries.
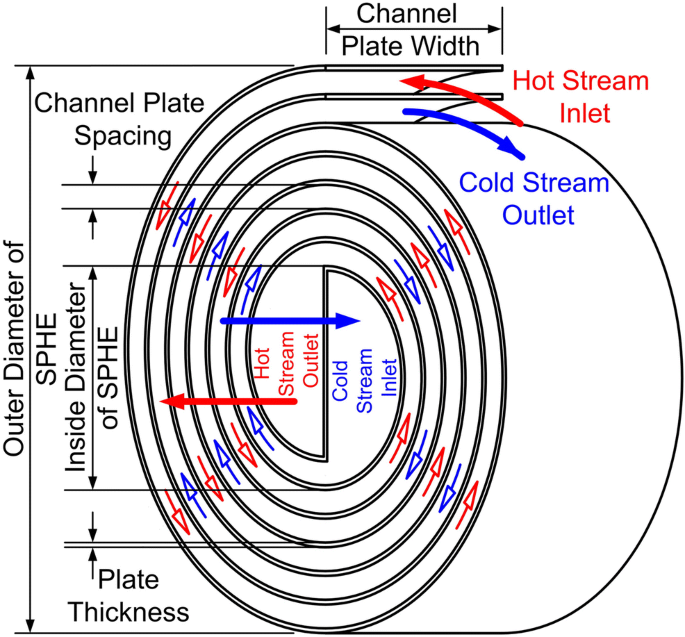
Pictured above: spiral-heat-exchanger
Design Considerations
The design of a spiral heat exchanger involves several key factors:
- Channel Width: The width of the channels affects the flow pattern and heat transfer rate.
- Channel Depth: The depth of the channels influences the pressure drop and heat transfer.
- Number of Turns: The number of turns in the spiral affects the overall heat transfer area and pressure drop.
- Material Selection: The materials of construction should be selected based on the fluid compatibility and temperature requirements.
- Gasket Material: The gasket material should be selected to provide a good seal and resist the operating conditions.
Applications
Spiral heat exchangers are used in various industries, including:
- Oil and Gas: Cooling and heating of fluids in refineries and petrochemical plants.
- Chemical Processing: Heating and cooling of reactive fluids and slurries.
- Food Processing: Pasteurization and sterilization of food products.
- Power Generation: Condensing steam in power plants.
- Wastewater Treatment: Heating and cooling of wastewater.
Spiral heat exchangers offer a compact and efficient solution for a wide range of heat transfer applications, especially those involving challenging fluids and high-pressure conditions.
By understanding the design principles and advantages of spiral heat exchangers, engineers can select and design these heat exchangers to meet the specific needs of a particular application.