U-Tube Heat Exchangers
A Reliable and Efficient Solution
U-tube heat exchangers are a type of shell and tube heat exchanger commonly used in various industries, including oil and gas, chemical processing, power generation, and HVAC systems. They are known for their reliability, efficiency, and ease of maintenance.
How They Work
In a U-tube heat exchanger, the tubes are bent into a U-shape, with both ends of each tube connected to the same tube sheet. This design allows for thermal expansion and contraction, reducing the risk of tube failures. One fluid flows through the tubes, while the other fluid flows through the shell. Heat is transferred between the two fluids through the tube walls.
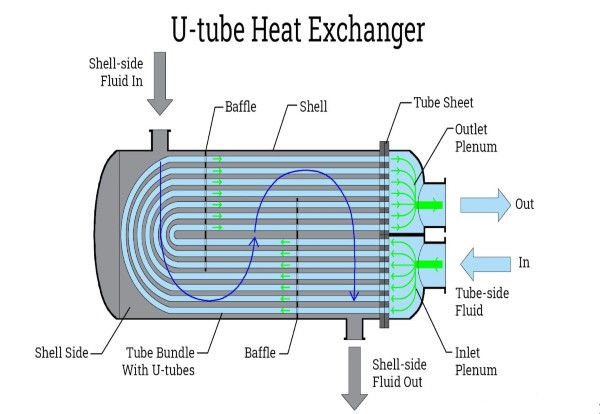
Pictured above: U-Tube Heat Exchanger Illustration
U-Tube Heat Exchanger Design
The biggest difference about u tube heat exchanger compared with other types of heat exchanger is the tube buddle structure, the longer the tube diameter is , the longer the minimum bending radius is. And the u tube heat exchanger bending radius should not less than two times the outer diameter of the heat exchanger tube.
U tube heat exchanger usually designed according to the ASME Code, Section VIII, Division 1. This high load U tube heat exchanger can prevent the stress damage caused by container inflation during the process of heating or cooling. As one end of the tube bundle is float, the heat exchanger can be guaranteed safety even under the extreme heat cycle. It is a ideal design method when the heat medium is steam.
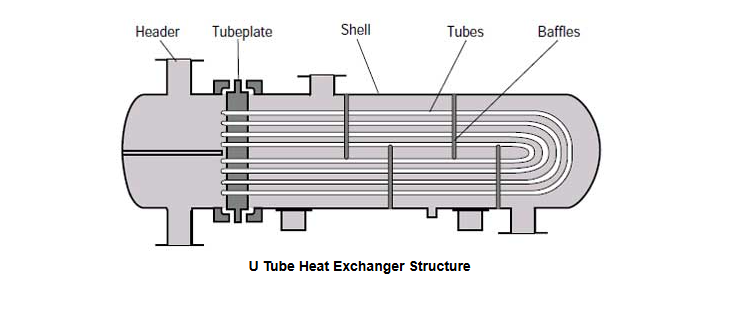
Pictured above: U-Tube Heat Exchanger Illustration
Advantages vs Disadvantages of U-Tube Heat Exchangers:
Advantages:
- Reliable Operation: The U-tube design allows for thermal expansion and contraction, reducing the risk of tube failures.
- Ease of Maintenance: The U-tube design makes it easier to clean and replace tubes.
- Versatility: Can handle a wide range of fluids and temperature differences.
- High Thermal Efficiency: The U-tube design provides efficient heat transfer.
Disadvantages:
- Complex Design: Can be more complex to design and manufacture than other types of heat exchangers.
- Potential for Vibration: The U-tube design can be susceptible to vibration, especially at high flow rates.
Key Considerations for Design and Selection:
- Tube Material: The tube material should be selected based on the fluid compatibility and temperature requirements.
- Tube Pitch: The spacing between the tubes can affect the heat transfer performance.
- Baffle Design: The baffle design can influence the flow pattern and heat transfer efficiency.
- Tube Sheet Thickness: The tube sheet thickness must be sufficient to withstand the operating pressure.
- Expansion Joint Design: The expansion joint must be designed to accommodate thermal expansion and contraction.
U-tube heat exchangers are a valuable tool for heat transfer in many industries. Their reliability, efficiency, and ease of maintenance make them a popular choice for a wide range of applications.
By carefully considering these factors, engineers can select and design U-tube heat exchangers that meet the specific needs of a particular application.