Waste Heat Recovery Boilers: Smarter Steam from Process Heat
Learn how waste heat recovery boilers work, their benefits, and what inspectors look for to ensure safety and code compliance.
What Are Waste Heat Recovery Boilers?
Waste heat recovery boilers (WHRBs) capture hot exhaust gases from industrial processes or engines and use that heat to generate steam or hot water — without burning additional fuel.
They convert wasted thermal energy into useful steam, improving efficiency and reducing emissions across refineries, gas turbines, furnaces, incinerators, and more.
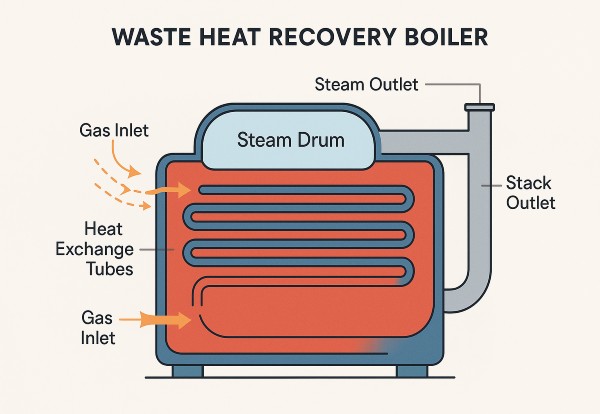
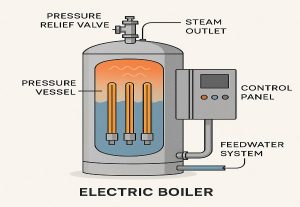
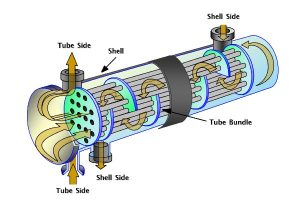
Pictured above: Waste Heat Recovery Boilers Work
How Do They Work?
A WHRB sits in the path of a hot gas stream (like from a combustion engine or furnace). Instead of venting the exhaust directly into the atmosphere, the system routes it through heat exchange surfaces in the boiler. This heats the boiler water and creates steam — all without lighting a burner.
Key Components:
- Gas inlet & ducting from the heat source
- Steam or hot water drum
- Tube bundles or economizer coils
- Bypass dampers (optional for temp control)
- Stack outlet
The system may be designed for supplementary firing — allowing a burner to boost output if needed.
Why Choose Waste Heat Recovery?
✅ Reduced fuel consumption — lower energy bills
✅ Lower emissions — ideal for ESG and decarbonization goals
✅ Improved plant efficiency
✅ Payback through energy savings
✅ Compact integration with existing processes
They’re an easy win for energy-conscious facilities — especially in industries that generate consistent high-temp exhaust.
What Do Inspectors Look For in WHRBs?
Because WHRBs handle high-temp gas flow and pressure-retaining vessels, inspections are just as important as with traditional boilers.
Authorized Inspector teams focus on:
- Thermal fatigue or creep damage in tubes and headers
- Tube fouling or slag build-up from dirty exhaust
- Steam drum integrity and NDE reports
- Flow-induced erosion in bends or at gas inlets
- Pressure relief devices sized for heat input
- ASME Section I compliance for steam service
- NBIC for any repairs or alterations
Designs with bypass or supplementary firing may have additional code considerations.
Code Coverage for Waste Heat Recovery Boilers
Most WHRBs fall under ASME Section I (Power Boilers) if they produce steam above 15 psig. Supplementary fired systems may also invoke Section VIII or B31.1 for piping and unfired vessels.
All alterations or repairs require NBIC R-Stamp documentation and inspection sign-off — and we’re your go-to team for that.
Where You’ll Find WHRBs in Use
- Gas turbines & engines (co-gen or combined cycle plants)
- Industrial furnaces & kilns
- Chemical process plants
- Refineries & incinerators
- Steel & glass manufacturing
If your plant runs hot — there’s a good chance waste heat recovery can help.