Understanding Water-Tube Boilers: Design, Applications & Inspection Essentials
Explore how water-tube boilers work, their advantages, and key inspection focus points to stay ASME- and NBIC-compliant.
What Are Water-Tube Boilers?
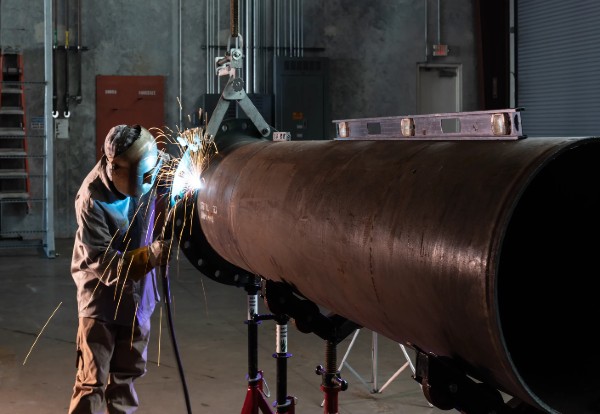
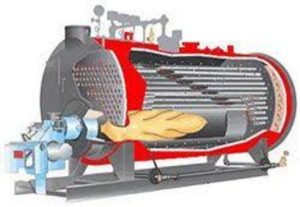
A water-tube boiler is a type of boiler where water circulates inside the tubes, and hot combustion gases flow around the outside of those tubes. This design is ideal for high-pressure applications and large steam outputs, making it the go-to choice for power plants, refineries, chemical processing, and other heavy-duty industries.
Pictured above: Water-Tube Boilers
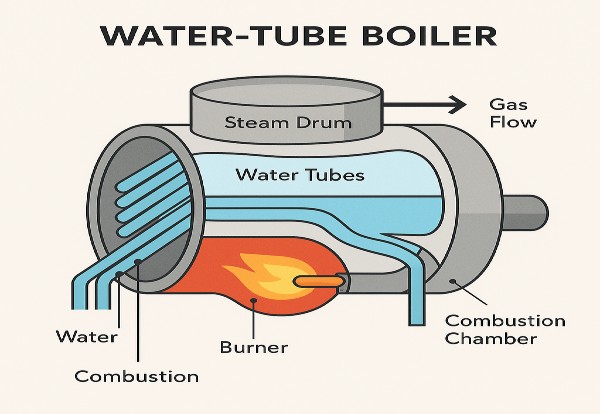
How Water-Tube Boilers Work
The basic operation flips the script on fire-tube boilers. Instead of hot gases flowing through tubes in a water-filled shell, water-tube boilers have water flowing through tubes while hot combustion gases flow over them.
Key Components:
- Drum (steam & mud drums) – collects steam or sediment
- Water tubes – carry feedwater and generate steam
- Headers – distribute water to the tubes
- Burner & combustion chamber – heat source for gas flow
- Economizer / Superheater (optional) – improves efficiency
This design makes it easier to handle high pressures and rapid load changes.
Advantages of Water-Tube Boilers
✅ Higher pressure capacity — ideal for industrial steam generation
✅ Faster response time to load changes
✅ Smaller water content — reduces explosion risk
✅ Modular configurations for tight or customized installations
✅ Efficient heat transfer due to tube surface area
Key Inspection Areas
Water-tube boilers require diligent inspection and maintenance due to their complex structure and high-pressure service.
- Internal inspection of steam drum and mud drum
- Tube scaling or erosion — especially near bends
- Cracking in rolled tube ends
- Welded joints on headers and nozzles
- Drainage and venting provisions
- Compliance with ASME Section I or Section IV depending on service
- NBIC repair/alteration records
Inspections may require disassembly, borescope access, or ultrasonic thickness testing depending on operating conditions.
Code Compliance
Most high-pressure water-tube boilers fall under ASME Section I (Power Boilers). For repairs, alterations, and rerating, compliance with the NBIC is essential — and that’s where we come in.
Should You Use a Water-Tube Boiler?
If you’re operating in a high-pressure environment, have large steam demand, or need responsive performance — water-tube boilers may be the better fit over fire-tube systems. They’re built for power and performance, but that also means more complexity in inspections and repairs.
Whether you’re commissioning a new boiler, updating documentation, or planning a repair — contact our Partner site J Lowry, LLC. They have the tools and experience to make sure your water-tube boiler is code-compliant and safe.
👉 www.jlowryllc.com
📞 281-995-0552